The Science Behind Dog Years to Human Years
The Science Behind Dog Years to Human Years
Blog Article
Understanding your dog's age in individual decades is more than a driving curiosity. It gives understanding into your pet's living point, helping you cater with their health, diet, and task needs more effectively. But as the widely-known Dog age 5 in human years method is popular, it doesn't completely reveal reality.
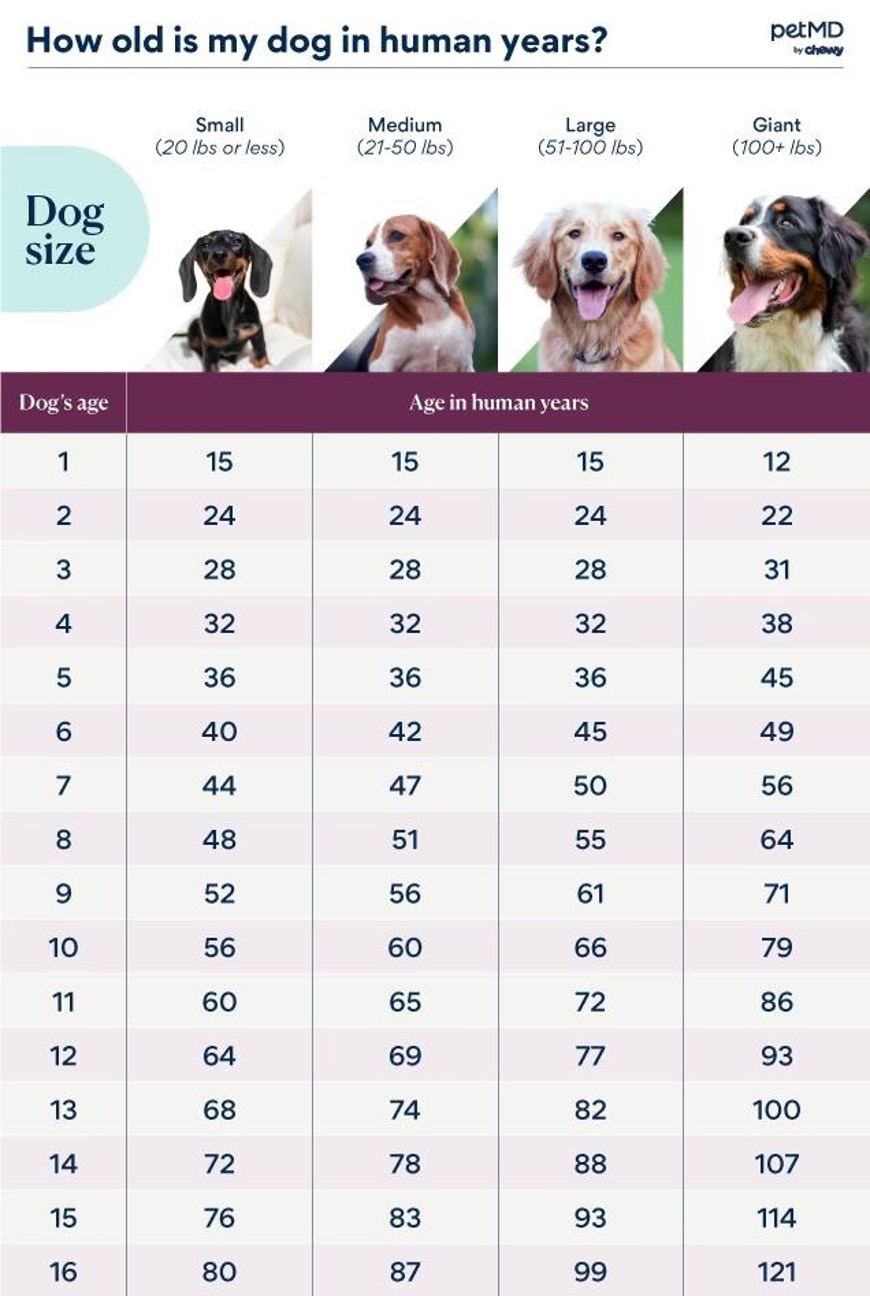
The Technology Behind Pet Years
The 7-to-1 principle oversimplifies how pets age. The pace of ageing ranges based on a dog's size, type, and their early development. Smaller breeds have a tendency to age slower and live lengthier, while greater breeds age rapidly and routinely have shorter lifespans.
Scientists at the University of Colorado developed a examine predicated on a dog's epigenetic clock (how DNA improvements around time) to evaluate ageing more accurately. According with their findings, a 1-year-old dog is around equivalent to a 30-year-old individual due to quick growth in the early years. By the time canine is 2 years of age, their human age is around 42. After this stage, the aging process decreases significantly.
A Breed-Specific Description
Here is a standard perspective on ageing across breeds:
Little Breeds (e.g., Dachshunds, Chihuahuas)
These dogs era slowly, and by their first year, they might be akin to a 15-year-old human. By the 2nd year, they're approximately 24 in human years. Each future year adds 4-5 human years.
Moderate Breeds (e.g., Bulldogs, Beagles)
Medium-sized dogs follow a somewhat quicker trajectory than smaller dogs. By age 2, they may be about 28 human years of age, with each following year equating to 5-6 individual years.
Large Breeds (e.g., Labrador Retrievers, Shepherds)
Bigger breeds display visible accelerated aging. A 1-year-old large dog's development correlates to a 15-year-old human, progressing to 49 human years by age 5.
Tailoring Attention to Their "Human Age"
By calculating your dog's human-equivalent age, you'll get a sharper knowledge of how to handle their life stage. For instance:
Pups (human baby equivalent): Give attention to education and socialization.
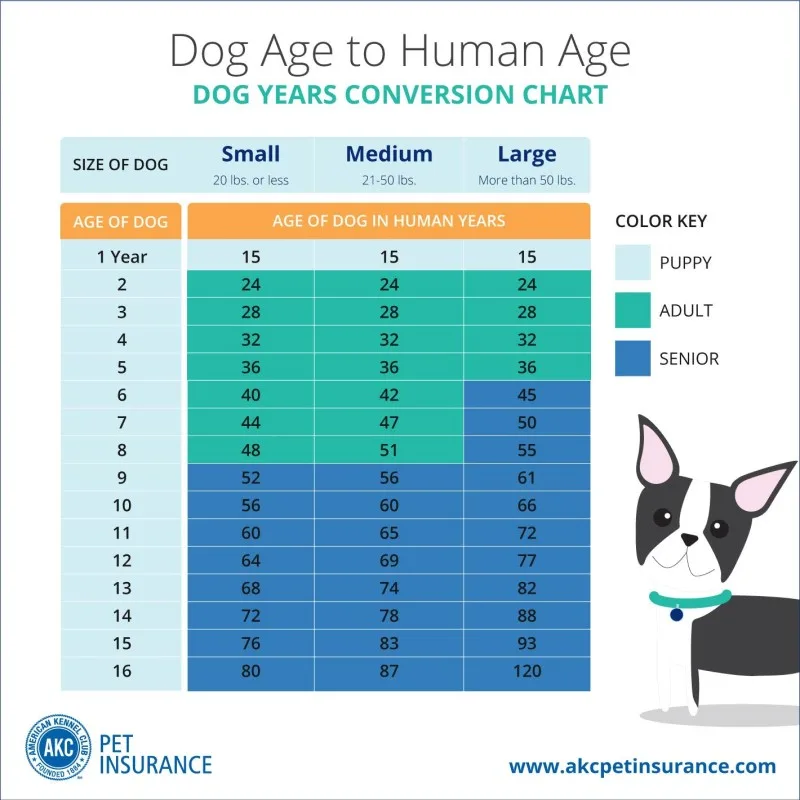
Adult dogs (human late 20s to 50s equivalent): Maintain their energy with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Elderly dogs (human 60+ equivalent): Spend particular attention to combined wellness, typical veterinarian visits, and smoother diets.
The connection of dog years to individual years offers puppy homeowners the knowledge they need to ensure their furry buddies stay the happiest and healthiest lives possible.
Report this page